Struts2 Action访问Servlet API的两种方式(附带实例) 图片看不了?点击切换HTTP 返回上层
在 Struts2 中,虽然 Action 已经与 Servlet API 完全分离,但在实现业务逻辑时,还是经常要访问 Servlet API 中的对象。
通常开发时需要访问 Servlet API 中的 HttpServletRequest、HttpSession 和 ServletContext 三个接口,它们分别对应 JSP 内置对象 request、session 和 application。
在 Struts2 中,访问 Servlet API 通常采用两种方式,分别是通过 ActionContext 访问和通过 ServletActionContext 访问,本节将针对这两种访问方式进行讲解。
要访问 Servlet API,可以通过如下示例代码方式进行:
在上述示例代码中,通过 ActionContext 类中的方法调用,分别在 request、application 和 session 中放入了("name","mengma")键值对。通过代码可以看到,ActionContext 类可以非常简单地访问 JSP 内置对象的属性。
为了让读者更好地掌握如何通过 ActionContext 类访问 Servlet API,下面通过具体的案例演示 ActionContext 的使用,具体步骤如下。
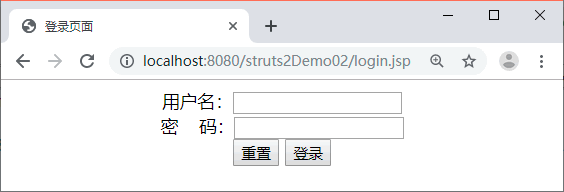
图 1 登录页面
在图 1 中输入用户名“admin”和错误的密码“123”后,单击【登录】按钮,结果页面如图 2 所示。
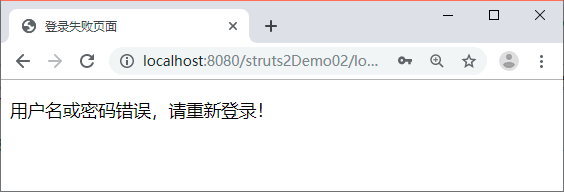
图 2 登录失败页面
在图 1 中输入用户名“admin”和正确的密码“123456”后,单击【登录】按钮,结果页面如图 3 所示。

图 3 登录成功页面
从图 3 中可以看出,在 Action 中放入 ActionContext 的 key-value 键值对都被取出来了,说明通过 ActionContext 类能够访问 Servlet API。
下面通过案例讲解如何通过 ServletActionContext 访问 Servlet API。
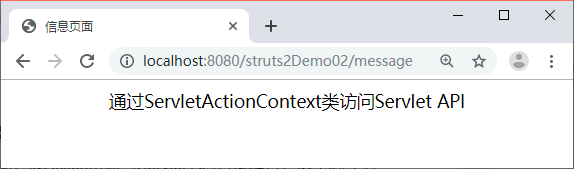
图 4 登录页面
从图 4 中可以看出,使用 ServletActionContext 类也可以在 Action 中访问 Servlet API。虽然如此,该 Action 依然与 Servlet API 直接耦合,这不利于程序的解耦。因此,建议在开发中优先使用 ActionContext,以避免和 Servlet API 耦合。
通常开发时需要访问 Servlet API 中的 HttpServletRequest、HttpSession 和 ServletContext 三个接口,它们分别对应 JSP 内置对象 request、session 和 application。
在 Struts2 中,访问 Servlet API 通常采用两种方式,分别是通过 ActionContext 访问和通过 ServletActionContext 访问,本节将针对这两种访问方式进行讲解。
通过 ActionContext 访问
ActionContext 是 Action 执行的上下文对象,在 ActionContext 中保存了 Action 执行所需要的所有对象,包括 request、session 和 application 等。ActionContext 类访问 Servlet API 的几个常用方法如表 1 所示。| 方法声明 | 功能描述 |
|---|---|
| void put(String key, Object value) | 将 key-value 键值对放入 ActionContext 中,模拟 Servlet API 中的 HttpServletRequest 的 setAttribute() 方法 |
| Object get(String key) | 通过参数 key 查找当前 ActionContext 中的值 |
| Map<String, Object> get Application() | 返回一个 Application 级的 Map 对象 |
| static ActionContext getContext() | 获取当前线程的 ActionContext 对象 |
| Map<String, Object> getParameters() | 返回一个包含所有 HttpServletRequest 参数信息的 Map 对象 |
| Map<String, Object> getSession() | 返回一个 Map 类型的 HttpSession 对象 |
1 2 3 4 | ActionContext context = ActionContext.getContext();context.put("name","mengma");context.getApplication().put("name","mengma");context.getSession().put("name","mengma"); |
为了让读者更好地掌握如何通过 ActionContext 类访问 Servlet API,下面通过具体的案例演示 ActionContext 的使用,具体步骤如下。
1)创建项目
在 MyEclipse 中创建一个名称为 struts2Demo02 的 Web 项目,将 Struts2 所需的 JAR 包复制到项目的 lib 目录中,并发布到类路径下。2)创建页面文件
在 WebContent 目录下分别创建登录页面 login.jsp、登录成功页面 success.jsp 和错误显示页面 error.jsp,如 login.jsp、success.jsp 和 error.jsp 所示。① login.jsp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 | <%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=utf-8" pageEncoding="utf-8"%><!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"><html><head><title>登录页面</title><style type="text/css"> input[type=text],input[type=password]{width:150px}</style></head><body> <div align="center"> <form action="login" method="post"> 用户名:<input type="text" name="username"/><br/> 密 码:<input type="password" name="password"/><br/> <input type="reset" value="重置"/> <input type="submit" value="登录"/> </form> </div></body></html> |
② success.jsp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | <%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=utf-8" pageEncoding="utf-8"%><!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"><html><head><title>登录成功页面</title></head><body> <p>${success }<br/></p> <h2>用户登录信息</h2> 用户名:${username }<br/> 密码:${password }<br/></body></html> |
③ error.jsp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | <%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=utf-8" pageEncoding="utf-8"%><!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"><html><head><title>登录失败页面</title></head><body> <p>${error }<br/></p></body></html> |
3)添加过滤器
在 web.xml 文件中配置 Struts2 的核心过滤器,配置后的代码如下所示。1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:web="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="3.0"> <filter> <filter-name>struts2</filter-name> <filter-class> org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ng.filter.StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter </filter-class> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>struts2</filter-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping></web-app> |
4)创建 Action
在 src 目录下创建一个名称为 com.mengma.action 的包,在该包中创建一个名称为 LoginAction 的类,该类主要用于业务逻辑处理,其代码如下所示。1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 | package com.mengma.action;import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext;import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;public class LoginAction extends ActionSupport { private String username; // 用户名 private String password; // 密码 // username的getter和setter方法 public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } // password的getter和setter方法 public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } @Override public String execute() throws Exception { // 获取ActionContext对象 ActionContext context = ActionContext.getContext(); if ("admin".equals(username) && "123456".equals(password)) { // 将用户名和密码信息放入context对象中 context.put("username", username); context.put("password", password); context.put("success", "用户登录成功!"); return SUCCESS; } else { // 定义登录失败的错误信息 context.put("error", "用户名或密码错误,请重新登录!"); return ERROR; } }} |
5)创建配置文件
在 src 目录下创建 struts.xml 文件,编辑后如下所示。1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC "-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.3//EN" "http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.3.dtd"><struts> <package name="default" extends="struts-default"> <action name="login" class="com.mengma.action.LoginAction"> <result name="success">/success.jsp</result> <result name="error">/error.jsp</result> </action> </package></struts> |
6)运行程序并查看结果
启动 Tomcat 服务器,在浏览器的地址栏中输入地址 http://localhost:8080/struts2Demo02/login.jsp 访问 login.jsp 页面,浏览器的显示结果如图 1 所示。
图 1 登录页面
在图 1 中输入用户名“admin”和错误的密码“123”后,单击【登录】按钮,结果页面如图 2 所示。

图 2 登录失败页面
在图 1 中输入用户名“admin”和正确的密码“123456”后,单击【登录】按钮,结果页面如图 3 所示。

图 3 登录成功页面
从图 3 中可以看出,在 Action 中放入 ActionContext 的 key-value 键值对都被取出来了,说明通过 ActionContext 类能够访问 Servlet API。
通过 ServletActionContext 访问
除了通过 ActionContext 类访问 Servlet API 以外,Struts2 框架还提供了 ServletActionContext 类访问 Servlet API,该类中的方法都是静态方法,其常见方法如表 2 所示。| 方法声明 | 功能描述 |
|---|---|
| static PageContext getPageContext() | 获取 Web 应用的 PageContext 对象 |
| static HttpServletRequest getRequest() | 获取 Web 应用的 HttpServletRequest 对象 |
| static HttpServletResponse getResponse() | 获取 Web 应用的 HttpServletResponse 对象 |
| static ServletContext getServletContext() | 获取 Web 应用的 ServletContext 对象 |
下面通过案例讲解如何通过 ServletActionContext 访问 Servlet API。
1)创建 MessageAction 类
在 struts2Demo02 项目中的 com.mengma.action 包下创建 MessageAction 类,编写后的代码如下所示。1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | package com.mengma.action;import org.apache.struts2.ServletActionContext;import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;public class MessageAction extends ActionSupport{ public String execute() throws Exception{ ServletActionContext.getRequest().setAttribute("message","通过ServletActionContext类访问Servlet API"); return SUCCESS; }} |
2)配置 struts.xml
在 package 元素中添加一个名称为 message 的 action 配置信息,添加代码如下所示:
<action name="message" class="com.mengma.action.MessageAction">
<result name="success">/message.jsp</result>
</action>
3)创建 message.jsp 页面
在 WebContent 目录下创建一个名称为 message.jsp 的页面,通过 EL 表达式访问存放在 Request 对象中键值为 message 的值,其页面主体部分代码如下所示:<div align="center">${requestScope.message }</div>
4)运行程序并查看结果
启动 struts2Demo02 项目,在浏览器的地址栏中输入地址 http://localhost:8080/struts2Demo02/message 后,浏览器的显示结果如图 4 所示。
图 4 登录页面
从图 4 中可以看出,使用 ServletActionContext 类也可以在 Action 中访问 Servlet API。虽然如此,该 Action 依然与 Servlet API 直接耦合,这不利于程序的解耦。因此,建议在开发中优先使用 ActionContext,以避免和 Servlet API 耦合。
